Bronze characteristics and application. What is bronze and what is it made of? How to clean bronze products in everyday life
Bronze is an alloy of copper and special additives that are necessary to give the metal certain technological properties. Bronze may contain the following components: Sn (tin), Mn (manganese), Be (beryllium), Pb (lead), Si (silicon), Cr (chromium), P (phosphorus), Fe (iron) and other elements.
Bronze alloy is resistant to abrasion, corrosion, aggressive environments such as sea water. These properties are achieved by adding alloying components in certain proportions. The ratio of components is regulated by regulatory documents: GOST, industry standards, methods, enterprise standards.
Alloy classification
In accordance with the presence of alloying components in the composition, it is customary to distinguish the following types of bronzes:
- tin - the main alloying component in them is tin;
- not containing tin at all, that is, tinless.
In addition to the composition of bronze, there is another criterion for their classification - technological parameters. Bronzes stand out:
- deformable, designed for pressure treatment;
- foundries for the manufacture of castings.
Main alloying components
The main component that determines most of the technical characteristics of bronzes is copper. To give the alloy the necessary parameters, special additives are used - alloying components. One of the common alloying components found in bronze is tin. It was from tin bronze that bells were cast and called "bell" bronze.
Also as an alloying element can be used:
- Be is beryllium. Increases the strength of bronze.
- Si - silicon and Zn, zinc to increase the resistance of the surface to abrasion. The same elements increase the fluidity of bronzes, which has a positive effect on the quality of casting.
- Pb is lead. Increases the anti-corrosion properties of the metal.
- Al - aluminum. Increases corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance at high temperatures and reduces metal reaction with sulfur compounds and engine exhaust products.
Brands of bronzes
Bronzes are marked with the abbreviation "Br", as well as the addition of a letter or several letters that indicate alloying additives. The volume of alloying additives is determined by GOSTs.
Different brands of bronzes have their own individual characteristics: chemical composition, technical characteristics, scope. By marking bronzes, you can find out what components they include, and using special tables to determine the purpose of this alloy and its technological parameters.
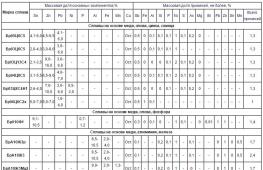
Marking of alloys on the example of tin bronzes
Some grades of tin bronzes are shown in the table below. Here you can also find important technological parameters of the alloy, as well as the scope of each specific brand of bronze.
This table also indicates the method of casting bronzes. "K" in the corresponding column means that casting was carried out in a mold, "P" - casting was carried out in a sand mold.
The "brand" column shows the names of the alloys. "Br" in the brand name denotes bronze, then the alloying components present in the alloy are indicated.
Based on the markings, it is clear that the metal grades listed in the table contain tin. Some, in addition to tin, contain zinc, lead and phosphorus.
The percentage of bronze components
The percentage of elements, as well as the chemical composition, is embedded in the abbreviation of the alloy grade. It does not indicate the percentage of the main element - copper, but indicates the content of all alloying elements as a percentage.
For example, in the BrO3Ts12S5 brand, the content of the components is as follows:
tin - 3%;
zinc - 12%;
lead - 5%;
the remaining 80% is copper.
The percentage of copper in the alloy affects its color. The more copper, the brighter the golden color of the bronze. At a copper content of 50%, the color of the alloy will become white, close to the color of silver. In accordance with the tasks set, it is possible to obtain a different color of the metal by varying the percentage of alloying elements and copper.
Some varieties of bronze alloys
The most commonly required are tin, beryllium, silicon and aluminum bronzes.
Tin bronze
Tin bronze contains tin as the main alloying component. It may also contain phosphorus, zinc, lead, nickel, etc.
The table shows the limiting content of elements in some grades:

As can be seen from the table, the alloys contain at least 80% copper. With an increase in the volume of tin in the alloy, its properties also change:
- the hardness and strength of the metal increases;
- plasticity decreases;
- impact strength decreases;
- increased fatigue strength.
One of the alloying components is P (phosphorus). This element is called alloying if its content is more than 0.1%.
Phosphorus, when it enters the copper alloy, deoxidizes the copper. In addition, it is phosphorus as an alloying additive that increases the wear resistance of the metal. This composition also has a downside. Phosphorus, when its content is exceeded, reduces the ductility of the resulting metal. Therefore, when adding phosphorus as an alloying component to wrought tin bronze, it is extremely important to strictly adhere to GOST and other regulatory documents.
Another alloying component is Zn (zinc). It is added to bronze that does not contain phosphorus. Zinc is introduced in an amount that can dissolve. Lead can often be added along with zinc. Lead is slightly soluble, the resulting alloys BrOTsS4-4-2.5 and BrOTsS4-4-4 are solid solution crystals and undissolved lead inclusions. The addition of lead increases the anti-friction properties of the metal and the possibility of cutting it. However, lead as an alloying element reduces some of the other mechanical properties of the resulting metal.
Ni (nickel) may also be added. The element increases strength, ductility and deformability.
beryllium bronze
This type includes tinless dispersion-hardened alloys of copper and beryllium. This means that the solubility of the alloying element is directly dependent on temperature. Hardening is carried out from a single-phase region, that is, immediately from the melt. It is very important to choose the right process temperature to be used. It is this value that determines how well the melt will pass into a solid solution and how homogeneous it will be, which is important for imparting specific properties to the metal. The optimum hardening temperature is 760-800 °C. With an increase in temperature over the specified range, there is a possibility of an increase in the grain size of the metal and, as a result, a decrease in technological parameters. Temperatures below this range do not allow the solid solution to be saturated with beryllium to the required degree.
The cooling rate of the solution should be at least 30-60 degrees per second. This is necessary to prevent the decomposition of components in the solid solution. Ni (nickel) and Co (cobalt) can sometimes be added as an additional dopant to lower the cooling rate limit. These additives increase the stability of the solid solution in case of supercooling. Magnesium can be used for the same purposes.
The following alloys are most often used in industry and production:
- BrB2 - with a beryllium content of 2%;
- MNB - copper-nickel-beryllium alloy, beryllium content does not exceed 0.8%
- MCB is the ratio of copper-cobalt-beryllium with the same content of beryllium as in MNB.
Both BrB2, and MNB and MKB have high ductility and strength, are easily subjected to bending and drawing, as well as other types of plastic deformation.

silicon bronze
This tinless alloy has in its composition Cu (copper) in the amount of 80%, Zn (zinc) 20% and Si (silicon) about 3% and 1% manganese (BrKMts-3-1), shows resistance to compression and tension deformation. High mechanical and antifriction properties, ductility at low temperatures allows this alloy to be used for antifriction parts, springs, bearings, etc.
aluminum bronze
Aluminum bronze contains aluminum as an alloying component. The aluminum content can reach 12%. Depending on the aluminum content, the properties of the resulting metal also change.
For example, single-phase bronze, in which aluminum up to 9.4% is easily subjected to pressure deformation at any temperature. This is due to its high plasticity. An example of such a brand is BrA7.
The addition of aluminum as an alloying component significantly increases the strength of the metal and its resistance to corrosion in difficult conditions: salt water, high humidity, etc. This type of metal is used for offshore oil platforms.
Al also has a significant effect on the thermal conductivity of the metal. With an increase in the aluminum content, the thermal conductivity of the resulting metal decreases, if we compare this parameter with pure copper. The addition of even 10% Al reduces the thermal conductivity of copper by 390-401 W/(m*K) to 75 W/(m*K). The addition of additional alloying components further reduces the thermal conductivity.
Thus, the following conclusions can be drawn: the technological parameters of bronzes depend on what alloying components and in what ratio were introduced in the manufacture of the metal. The main component is copper, the percentage of alloying additives is regulated by GOSTs and other regulatory documents.
Bronze is an alloy of two metals. It is widely used in various areas of human life: from the automotive industry to interior design.
What is bronze made of?
It is copper alloyed with tin. Also, instead of the latter, aluminum, manganese, beryllium and other elements can be used for its manufacture. In addition, the composition contains various impurities in small quantities.
Brass is also created on the basis of copper, for which zinc is used.
Nowadays, there are grades of this alloy, which have a different composition. Bronze of different types can vary greatly. Different brands are used for different purposes.
The color of this alloy directly depends on the percentage of copper and tin of which it is composed. With a decrease in the amount of the first and an increase in the second, the color loses its red and acquires a gray tint.
When did bronze first appear?
This alloy has been known since very ancient times. It began to be made and used much earlier than iron. Only copper and tin were included in its composition. Bronze of that time did not contain impurities. It was first obtained about five thousand years ago, that is, in the III millennium BC. e. The period when this alloy was used is called the "Bronze Age". It lasted until the 1st millennium BC. e., that is, before the time when people learned to extract iron.
Bronze was widely used to make all sorts of items, including jewelry, figurines, weapons, and utensils.
Bronze. Composition and application

Rolled products are made from this alloy: rods, reinforcement, sheets, as well as all kinds of other products, for example, mesh, bearings, any parts of various equipment. Bronze is also used in construction and architecture for the manufacture of monuments and decorative elements. In addition, this alloy finds its application in plumbing - pipes are made from it.
The main group are tin bronzes. From the name it is clear that tin is one of the main metals that make up the composition. Bronze of this type is divided into two types: that for which high pressure is used, as well as foundry.
Processed pressure includes Br. OCS 4-4-2.5. It consists of tin in an amount of three to five percent, lead (from 1.5 to 3.5 percent), zinc (from three to five percent), and some iron (0.05%). Everything else is copper.
The same group includes bronze, the composition of which includes from six to seven percent tin, 0.1-0.25 percent phosphorus, as well as 0.02% iron and the same amount of lead. This is Br. OF 6.5-0.15.
The next group is foundry bronze. Iron supplements are not included in its composition. Bronze of this type is often used to make art objects, etc.

Br. OTSS6-6-3 consists of five to seven percent tin, 5.5-6.8 percent zinc and copper.
In the composition of Br. OTsSN3-7-5-1 includes 2.5-4.5 percent tin, 6.5-7.5 percent zinc, as well as 4.6-5.4% lead and 0.8-1.2% nickel.
Often in our time, tin began to be replaced by other metals, since it is cheaper. Such alloys form other groups.
Tin-free bronze is often not inferior in quality. Such types of it are widely used in the automotive industry and other similar industries.
Aluminum bronzes
This metal most often acts as a replacement for tin. Its amount in the alloy can be about 10 percent. Bronze, the composition and properties of which have been known since ancient times, is slightly different from aluminum. It is more expensive, since tin, which has been used for the production of this alloy since ancient times, has a higher cost than aluminum.
However, although it is cheaper, aluminum bronze still has high strength. It is mainly used to make bushings, bearings, and so on.
The most common brand of this group of bronzes is Br. AZHN10-4-4. Its composition includes 9.5-11 percent aluminum, 3.5-5.5 percent manganese and the same amount of iron. The rest is copper.
Beryllium bronzes
Such alloys contain about two percent beryllium.
They have increased strength and hardness, as they are subjected to special heat treatment, which improves the characteristics of the material. The main use of these bronzes is found in the manufacture of tools such as hammers, chisels, etc.
Silicon bronzes
This group of alloys contains 2-3 percent silicon in its composition. They are corrosion resistant and have good casting properties.
From this kind of material, tape, wire, springy products and the like are most often made.
Nickel bronzes
Nickel is present as an impurity. Among their main features are viscosity, good resistance to acids and high temperatures.
Patinated bronze
This species is also very common today. Patination of bronze gives it the effect of antiquity and plays a decorative function. But, besides this, it also protects the material from corrosion. The patination method of this alloy is similar to the technology. As a result of the procedure, a black one is obtained which has not been changed.

Brass
The composition of bronze and brass has one main common feature - the main component is copper. It is also the most important and widely used alloy based on this metal. However, zinc is used as the second element in this case, not tin. Also in small quantities there are additives in the form of lead, iron, silicon.
What additive is contained in a particular brand of brass can be understood from the marking, in which, after the letter L (which means "brass"), another one is introduced, for example, C (lead) in the designation LS59-1. From this we can understand that the alloy contains 59 percent copper, 1 percent lead, and the rest zinc.
The color of brass and its properties depend on the percentage of copper content in it. There are three main groups: red, yellow and white. Red contains in its composition more than 80 percent of copper, this type of brass is also called "tompac". It is used to make thin sheets.
In yellow, the percentage of copper is lower - 40-80%. It is mainly used for the production of keys, headsets, and it is also used in the automotive industry.

The white variety of brass contains 20-40% copper. It is very fragile, so it can only be formed by casting.
Bronze owes its high popularity not only to its decorative characteristics, but also to a number of other properties. Meanwhile, few of those who use this metal can name the composition of bronze, and in fact it determines the characteristics of this copper alloy.
Basic alloying additives
Bronze is a color that determines most of its characteristics. Man began to produce and use bronze for products for various purposes since ancient times, as evidenced by the results of archaeological excavations. Initially, bronze was used, the composition of which was enriched with tin. The alloys of this type include, in particular, the so-called bell bronze (bells were cast from it for many centuries).
In addition to bronzes containing tin in their composition, copper alloys are also actively used today, in which this chemical element is not present. Instead of tin as the main alloying additive in such copper alloys, the following are used:
- beryllium, which gives bronze increased strength;
- silicon and zinc - elements due to which the surface of a bronze product becomes very resistant to abrasion and improves the fluidity of bronze, which is especially important for casting operations;
- lead, which makes bronze resistant to corrosion;
- aluminum, endowing bronze with worthy anti-friction properties and high resistance to corrosion.
The question of what metal is necessarily present in any bronze can be answered unambiguously: it is copper.

The chemical composition of various grades of bronze (click to enlarge)
In addition to separation by chemical composition, there is a classification according to processing technology:
- deformable (used for the production of products that are processed by the plastic deformation method);
- foundry (products from them are produced by casting).
Modern industry produces many grades of bronze, which differ in their chemical composition and, accordingly, in their characteristics and scope. Many experienced craftsmen, even by the color of bronze, can determine what type it belongs to. However, not everyone is able to do this. The surest and easiest way to get information about what is contained in the bronze of a certain brand and what type it belongs to is to decipher the marking, which includes both alphabetic and numeric designations.

All brands of bronze alloys produced by modern enterprises in strict accordance with the requirements of regulatory documents (GOSTs) are listed in special tables, from which you can get information not only about the chemical composition of an alloy of a certain brand, but also about its scope and characteristics. However, even without using such tables, it is possible to determine the type of alloy and its chemical composition, if you know the principle by which its designation is formed.

Mechanical properties and applicability of tin bronzes (k - mold casting, p - sand casting)
You can understand that this is bronze, an alloy of copper, by the first letters “Br” present in the marking. After them, letters are placed, by which you can find out what other metals, except for copper, are contained in the chemical composition of this alloy. The regulatory document establishes the following rules for the designation of chemical elements present in bronze:

Characteristically, the marking of bronze of any brand does not indicate the amount of copper contained in its chemical composition. At the same time, the numbers present in the designation indicate the quantitative content (in whole fractions of a percent) of the remaining elements. Accordingly, the amount of copper contained in bronze of a certain grade is calculated as the difference between 100% of the total composition and the amount of additives. For example, bronze of the brand Br AZh 9-4 contains 9% iron and 4% aluminum, the remaining 87% is copper.

The amount of pure copper contained in the composition of bronze affects not only the technological and operational characteristics of the product, but also the color of its surface. So, products from the most common grades of bronze alloys, which include about 85% copper, are distinguished by a golden color. If the amount of copper is reduced to 50%, then the output may be white bronze, very similar in color to silver. If desired, gray and even black bronze can be obtained - this result can be achieved if the amount of copper in the alloy is reduced to 35% or less.
Many old bronze products, the surface of which is almost black, acquired it not because of the use of an alloy of a certain composition for their production, but as a result of the influence of time and various external factors (fires, prolonged exposure to damp earth, etc.). In ancient times, bronze production technologies simply could not exist, the composition of which is complemented by rare earth metals, giving it a rich black color.
Brands and areas of their application
Naturally, various chemical elements are introduced into the composition of any bronze not aimlessly, but in order to improve its properties. Thus, the content of such a metal as tin in bronze affects its plasticity. The more this metal is contained in the composition of bronze, the harder and, accordingly, the more brittle the alloy becomes. However, the most significant influence on the hardness and strength of bronze is exerted by such a chemical element as beryllium. Some grades of bronze alloys containing beryllium in their chemical composition surpass high-quality steels in their strength characteristics. If subjected to the hardening procedure, then along with high strength, it acquires elasticity, which makes it possible to manufacture springs, springs and membranes for various purposes from this material.

Properties and applications of beryllium bronzes (click to enlarge)
From bronze alloys, the chemical composition of which is enriched with aluminum, products are produced that must combine sufficiently high strength with exceptional corrosion resistance. Due to the characteristics of bronze alloys of this type, products made from them are successfully operated under the most unfavorable conditions (high humidity, exposure to sea water, etc.). In those cases when it is necessary to make a product from bronze, which will be subjected to significant shock and friction loads during operation, it is better to use alloys containing lead in their chemical composition. From such bronze, in particular, bearings used in mechanisms for various purposes are produced.

Bronzes, which, in addition to copper, contain silicon and zinc, are characterized by increased fluidity in the molten state, so they are used mainly for the production of complex parts by casting. A distinctive feature of this type is that during mechanical action on the products that are made of them, no sparks are formed. This quality is very important in many cases.
A relatively new type of bronze, which was developed in connection with the development of the oil industry, are copper alloys, the composition of which is enriched with aluminum and nickel. Such bronzes, which are distinguished by exceptional corrosion resistance, are often called marine bronzes, because products made from them are able to retain all their original characteristics even after long-term operation in salty sea water. It was possible to obtain such alloys, which are actively used for the production of elements of oil platforms installed on sea and ocean shelves, thanks to the development of the metallurgical industry.
Most of the brands of bronze alloys are not magnetized, which makes it possible to successfully use them for the production of electrical products.
How bronze is made
Over the long period of existence of bronze production technology, only tools and equipment have changed, but the essence has remained the same. As in ancient times, charge or bronze waste can act as a raw material for obtaining this copper alloy, and charcoal is a flux that prevents too intense oxidation of the metal in the molten state.

The melting process itself, as a result of which bronze is obtained, is performed in the following sequence.
- The crucible with the feedstock is placed in an oven preheated to the required temperature.
- So that the metal does not oxidize much after melting, crushed charcoal is added to it - a flux.
- After the metal is completely melted and warmed up well, phosphorous copper is introduced into its composition, which plays the role of an acid catalyst.
- After some exposure in a heated state, alloying and binding elements (ligatures) are added to the molten metal, after which the resulting alloy is thoroughly mixed.
- Before pouring the molten metal, phosphorous copper is again added to it, which in this case is necessary to reduce the activity of oxidative processes.
At all stages of production, it is necessary to carefully monitor the observance of the correct temperature regime in the furnace and the alloy itself. The amount of alloying and binding components added to the molten metal should also be controlled.
Everyone has heard or seen bronze, the composition of this metal alloy remains a mystery to many. This article describes the types, from which it is obtained and where it is used. They learned to get metal at the dawn of the third millennium BC. Since then, proportions have changed more than once, technology has improved, but has never lost its significance for human civilization. The metal has unique operational and decorative characteristics, which is why it is still used in various modern fields.
Bronze is an alloy of several components that determine its main characteristics. The result is a material that has no limits on application. The very first products were used by people who lived in Mesopotamia and Southern Iran. This is confirmed by archaeological finds. From what the mixture is obtained, what components are added by modern masters, you will learn from the next section.
Compound
In order to obtain a high-quality bronze alloy, the composition must consist of one or more base substances, as well as alloying additives. The main component is copper, and the rest are needed to improve the performance of the material. As an alloying component is used:
- manganese;
- tin;
- lead;
- chromium;
- phosphorus;
- iron.
Zinc and nickel are used in extreme cases, because such a combination with copper gives completely different alloys (brass and cupronickel, respectively).
The amount of additives in the mixture may be different. But this is what affects the color of the metal. For example, a fiery red hue indicates the presence of a large amount of copper. By cold steel color, you can understand that it contains no more than 35% in the mixture.
The number of additional elements should not exceed 2.5 percent of the total mass. In addition to copper, bronze contains other metals: tin, aluminum, lead, silicon and beryllium. Based on the element used, the combination is given a name. Whatever alloying additions are chosen, only copper, which determines most of the characteristics, remains constant.
The chemical composition of bronze determines how the alloy and grade will turn out. All types differ in the mass fraction of the main components and impurities. The exact quantities are given in a special table, where several are considered and the impurities used are indicated.

Properties and characteristics
From an alloy consisting of copper and tin, bells were cast a few years ago. To date, other types are actively used, which, in addition to tin, include other chemical elements. Each of them gives special qualities to bronze.
Alloys containing beryllium are characterized by increased strength. But silicon, as well as zinc, added in small quantities, improves the fluidity of the metal. Therefore, such a composition is often used in foundry cases, or they cover the surface of various products with it. Why do they become resistant to abrasion.
A small amount of zinc included in the total mass does not change the mechanical properties of the composition. The element reduces the cost of the finished material, therefore, sometimes up to 10% zinc is specially introduced in industry in order to reduce the cost of production.
Alloys containing lead are resistant to corrosion. Aluminum, as an alloying additive, endows the composition with anti-friction properties. What qualities the finished product will have depends directly on the presence of one or more additional elements in it, as well as on their quantity.
Bronze is a metal that has increased strength, corrosion resistance and wear resistance. Products from it are not afraid of atmospheric phenomena, ingress of salt water, various solutions containing organic acids. The alloy is suitable for welding and soldering, and also comes in various shades - from red to white.

It differs not only in chemical composition, but also in processing technology. Modern industry is familiar with such methods as: deformable and foundry. If a mixture is required that will withstand cold forging, then the components are processed in the first way. The alloy from which the products are cast is processed by the second method.
Today, there are many brands that differ in characteristics and scope. Experienced craftsmen who have been working with a mixture for a long time can determine what type it belongs to by a glance. But just interested people can get information by examining the marking, which consists of letters and numbers.
A description of the characteristics will help to better understand what the mixture is, but it is worth exploring more pros and cons. It has a lot more positive sides than negative ones. Therefore, the material has not lost popularity for such a long time due to the mass of excellent qualities. These include the fact that products made from such a metal can be remelted an unlimited number of times. At the same time, the alloy remains the same quality as after manufacture.
It is popular among sculptors, in the field of instrumentation and machine tools, because it gives minimal shrinkage. In order for it to yield to mechanical processing, the composition should not contain more than 5% lead. Since it is this component that provides lightweight chip breaking. The presence of phosphorus in the composition deoxidizes the mixture, but only if no more than 1% of the alloying component is added.
Tin bronze
Most often, tin is used as an additive to copper. After all, it is this component that gives copper special qualities. The combination with tin has the following properties:
- fusibility;
- hardness;
- elasticity.
The finished material is convenient for polishing, and due to the presence of additional components, it is often used for casting. The advantage of tin bronzes lies in a wide range of applications. But it all depends on the quantitative content of the elements.

Since this parameter changes performance. For example, when only 5% tin is added, the ductility decreases. If the amount of an element is quadrupled, the material becomes brittle. Depending on this, the finished product is used in different ways.
The mixture, where the proportion of tin exceeds 6 percent, is sent for casting, but it is not suitable for forging or rolling. The metal, which has a pleasant silvery-white color, contains 33% tin. If this parameter decreases / increases, then the shade of the material will also change, from red to yellow. Photos of non-ferrous metal can be seen in a variety of places, from school textbooks to modern museums.
Tinless bronze
If the mixture does not contain tin, then it is called special or tinless. In this case, elements such as:
- aluminum;
- iron;
- lead;
- silicon;
The scope of this combination is also extensive. But the mixture itself is very different from tin. The main difference lies in the superior quality and the fact that copper without tin has an even richer color range.
If you combine copper with aluminum, you get a mixture that wins in terms of quality. It also has high resistance to chemicals. The combination of copper with silicon and zinc gives the metal fluidity. Due to its liquid state, it is easy to process.
The beryllium type surpasses all others in elasticity and high hardness. The material also has such qualities as high weldability and chemical resistance. With this type it is convenient to work with a cutting tool. After high-quality processing, the following parts are made from it:
- membranes;
- springs;
- contacts with spring properties.
They are durable, simple and reliable in operation. This is not the whole list of products that are made by craftsmen.

Application
Thanks to experiments with the proportions of alloying components, it was found that the use of non-ferrous metal is possible almost everywhere. All because of the properties it possesses. For example, the aluminum look is used when metal pipes and bands are needed. Products are easy to cut, but at the same time they are not afraid of corrosion. Even when the pipes are in sea water, the conditions do not affect their quality. Lead bronze is used in the manufacture of bearings, as the alloy resists shock loads and has anti-friction properties.
When it is required to make parts of a complex shape that should not form sparks during operation, they remember the silicon-zinc mixture. The material can be shaped into any shape because it is highly fluid.
There are not only classic compositions, but also completely unique in their properties, which were discovered recently. Such material is aluminium-nickel bronze or marine bronze. The only property that this combination has in common with the classical one is the presence of copper as the main element. The material was obtained as a result of the development of foundry production and is used in the construction of platforms for oil production located in the seas and oceans. Fire pumps, whose metal parts are made of aluminum-nickel type, withstand specific environmental conditions.
The most famous way to use bronze is to create sculptures and other decorative objects. In homes or on the pages of fashion magazines, you can often see products such as:
- figurines;
- lamps;
- railings for stairs;
- grills for fireplaces.

Thanks to the casting look, it is possible to obtain the most complex castings that convey the surface of the template in great detail. Previously, the material formed the basis of almost all women's jewelry, but today its use in jewelry has noticeably decreased.
But plumbing, production of entrance and interior doors cannot do without bronze fittings. From a strong and beautiful mixture of components, reliable, durable overhead hinges, locks, handles, faucets and faucets are created. It is convenient and easy to work with it, so the craftsmen manage to produce elegant decor elements of any size and design.
Beryllium bronze is used to make products for aircraft navigation instruments, car circuits, because it can withstand dynamic variable loads. There was a place for the use of this species in the water supply, despite the high cost. It is used to produce structures for especially critical areas. Because they will last much longer and will not require urgent repairs.
Although new consumables have been invented, the metal is not losing ground. Because its application guarantees a high-quality result, regardless of the area. This is due to the properties and variety of products, due to which bronze is in great demand.
Bronze is a metal obtained by mixing melts of copper and some other metals and non-metals. As a rule, the amount of components additive to copper does not exceed three percent, but there are exceptions to this rule - zinc and nickel can be added in large quantities. Such alloys are called brass and cupronickel (melchior), respectively. In other alloys, zinc may also be present, but with a limitation: its amount should not exceed the sum of the remaining metals to be added. If this happens, the alloy will be brass.
This metal alloy appeared about five and a half thousand years ago. It was then that the Bronze Age began. And until that time, only copper was smelted - this metal was the basis of all tools. When it happened to combine melts of copper and tin, another metal was obtained, which was called bronze - it is an alloy of copper and tin, harder than the original metals. He immediately found wide application in all spheres of human life: they made edged weapons and kitchen utensils, mirrors and jewelry, coins and sculptors' creations from it.
Medieval bronze artisans cast bells for the needs of the church and cannons for the army. Specially made bronze was used for casting cannons. This technology existed until the nineteenth century. Below are interesting facts about bronze.
Manufacturing methods and characteristics
Physical Data
The characteristics of the alloy are determined by its chemical composition and may vary within certain limits. Bronze is less susceptible to corrosion and provides better metal-to-metal sliding than brass. It has higher strength and is less susceptible to atmospheric influences (water and air) and better resists salts and organic acids. It is easy to machine, it can be soldered and fastened by welding. Some physical characteristics of bronze:
- specific gravity from 7.8 to 8.7 tons / cu. meter;
- melting point of bronze - melts when heated from 930 to 1140 degrees;
- color changes from red - the color of copper, to white - the color of tin;
- wear resistance and good sliding on metal determines the scope of application as plain bearings, they work well in any temperature conditions;
- there is a high electrical conductivity and heat transfer, resistance to steam exposure, which contributes to the manufacture of parts for equipment operating in extreme situations.
How to make bronze
Melting and mixing of copper melts and additives of different metals, which make it possible to give the alloy certain required characteristics, leads to the production of such an alloy metal as bronze. In the manufacturing process electric ovens involved induction type and crucible forges, with their help you can make any alloys with copper.
Smelting is carried out with flux additives, while the initial raw material for smelting can be both copper ore and copper scrap. As a rule, copper scrap is added to the melt along with the added metal during the smelting process. When smelting only from copper ore, the following operations are performed:

When using copper scrap, the procedure for making bronze is the same.
Varieties
According to the ratio of the content of the main components of bronze - copper and tin, two main types are known: tin, when the main filler material is tin, and tinless, if tin is present in a very small amount.
Tin bronze
Classical or tin bronze- a universal material not only in industry, but also in other areas of human life. In this alloy, 80 parts of copper account for 20 parts of tin, it melts well, has high strength, is quite hard, does not corrode, is wear-resistant and helps to reduce the friction of metals.
These advantages of tin bronze lead to difficulties in several other respects: the alloy is difficult to forge and cut, sharpen sharp edges and stamp, but it is easy to make castings from it. The sediment during cooling of the casting does not exceed one percent, which allows the material to be used in artistic products of high precision.
To give the alloy additional properties, it may include additives of other metals and non-metals:
- zinc in an amount of up to 10% improves anti-corrosion properties, parts made of such an alloy are used in shipbuilding, where salt water is an aggressive medium;
- lead and phosphorus contribute to a better sliding of bronze products on other metals, such an alloy is easier to cut and stamp.
Tinless
 - sometimes the use of tin in an alloy is not allowed, and the required characteristics are obtained by adding other metals. Modern technologies make it possible to select additives in such a way that products made of bronze without tin completely replace products made of classical bronze.
- sometimes the use of tin in an alloy is not allowed, and the required characteristics are obtained by adding other metals. Modern technologies make it possible to select additives in such a way that products made of bronze without tin completely replace products made of classical bronze.
lead bronze- an alloy that perfectly slides over metal, withstands great pressure, is very durable and melts with difficulty. Its scope is bearings operating under high pressure.
Silicon- it is 97% copper, a little tin and five hundredths of a percent silicon, it is added to increase electrical conductivity and such bronze is used as cores of telephone cables. It is not magnetic, well soldered, elastic and resistant to low temperatures. Additionally, it may contain manganese.
beryllium- the hardest. This alloy is very resistant to corrosion and extreme temperatures, both plus and minus. It is a non-magnetic metal and there are no sparks from it during collisions. Additionally, nickel or cobalt can be added to it. Elastic products are made from the alloy - springs, membranes, plates.
Aluminum- the composition is simple, five percent aluminum, the rest is copper. The color of bronze is brilliant golden, it is resistant to chemicals - acids. It is durable in hardness and heat-resistant, retains its properties even at extremely low temperatures. It resists corrosion weakly and gives significant shrinkage during casting. For its beautiful color, it is used in jewelry production, the manufacture of coins and medals. Physical properties predetermine the use of the alloy in the details of automotive products, gunpowder and pyrotechnic production.
Marking
 What metals are in bronze? To find out the main composition of bronze allows its marking, developed on the basis of state standards. Example: BrOF 7. The first two letters are bronze; alloy composition: O is tin; Ph is phosphorus; 7 - additive content, in this case tin, since the content of the second additive substance is not indicated in the marking. Designations of other filler substances: A - aluminum, K - silicon. Mts is manganese, Zh is iron, and so on, according to the first letters of the additive.
What metals are in bronze? To find out the main composition of bronze allows its marking, developed on the basis of state standards. Example: BrOF 7. The first two letters are bronze; alloy composition: O is tin; Ph is phosphorus; 7 - additive content, in this case tin, since the content of the second additive substance is not indicated in the marking. Designations of other filler substances: A - aluminum, K - silicon. Mts is manganese, Zh is iron, and so on, according to the first letters of the additive.
It is not customary to indicate the percentage of copper content in the marking; it is calculated by calculation as the remainder of the difference. In the example, this is 93%. Its color depends on the chemical composition of bronze. The copper content of an alloy determines its color - the higher it is, the redder the bronze will be, and vice versa. If there is only 50% copper, and everything else is light additives, then the alloy will resemble silver in color.