What is the full pressure of the pump. Pressure, energy and cavitation characteristics of NM type pumps
Pumps
Lecture №1
Classification of hydraulic flowing machines
Hydraulic machines N.clamping machines that are reported by mechanical energy flowing through them ( pump)either receive part of the energy from the liquid and transmit it to the worker for useful use ( hydraulic engine).
Pumps for tensile pressure amplifiers typically have independent closed cooling contours in which the oil is cooled using a heat exchanger with a fan. In this case, cooling is valid regardless of the pump operation time. In addition, the use of the heat exchanger allows the use of evaporated energy to heat the premises in winter.
Today, pressure pumps are dominated among producers of water jet cutting devices. Pumps with amplifiers are produced with a capacity of 18 to 200 kW. 80% of rocker pumps are components intended exclusively for these pumps, which leads to unnaturally high prices for spent parts. Pressure enhancer pumps with pressure amplifiers are used in 80% of standard hydraulic parts, which significantly increases the competition between their suppliers. The most important advantage of connecting rod pumps is that they significantly reduce the cost of products, which allows them to be used in semi-professional equipment intended for companies where they will be used in random order when operational and operating costs do not matter.
Pumps are one of the most common varieties of machines. They are used for various purposes, starting the water supply of the population and enterprise and ending fuel supply in rocket engines. The hydraulic motigaves are of great importance in the energy sector.
Flowing hydraulic machines are characteristic of the fact that in them the exchange of energy between the machine and the liquid occurs during its movement. By the nature of energy transfer, all flowing hydraulic machines are divided into blowers, engines and transmissions.
If the user needs to compete in the service market, or if the water treatment process is intensive, it or it must be investing in a hydraulic machine with a pressure pump. Silent work is a smaller size - less oil is cheaper in production.
High operating costs - low durability - delicate design - reduction in pressure and efficiency - Open system Cooling - limited pressure adjustment - inverter energy loss - water treatment is required. Pumps with pressure increase.
Lower operating costs - longer service life - a wide range of pressure regulation - a closed cooling system - no need for water treatment - more high pressure And efficiency is the lack of losses in the inverter.
In the superchargers, the mechanical energy of the engine goes into the mechanical energy of the liquid. A typical example of superchargers are pumps and compressors, in the first energy transmission occurs to drip fluid, secondly - to gas.
In engines, on the contrary, the hydraulic energy of the fluid is transmitted to the actuator in the form of mechanical energy (rotational motion of the shaft or the return-translational movement of the piston). An example of engines in flow hydraulic machines are turbines, hydrobotes, hydraulic motors and others.
Lower work - large sizes - more oil - more expensive production. If you are looking for a washing workshop or if you are driving in dirty, hard-to-reach places, think about a slightly higher pressure cleaner. With this cleaning agent you can easily remove dry dirt, grass, fat and oil.
Purpose washers for the car - what to look
By buying a washing machine, you should pay attention to the material from which it was manufactured. The durability of materials will depend on the materials used. One of the most important parts Washers is the pump head. Heads can be made of aluminum, brass or plastic. The most durable material is brass. Washers with brass pump heads are one of the most durable. If you do not use a washing machine very often, a sufficient pump equipped with an aluminum or plastic pump head.
In transmissions, both principles of energy transformation are combined, they take a qualitative change in mechanical energy (torque, revolutions). Example of gear are hydromeflues, hydraulic drives.
On the principle of action, all hydraulic flowing machines are divided into dynamic and volumetric.
Dynamic machines (a typical example - centrifugal pump) have the following features:
Other components included in the washing machine are the pressure line, furma, nozzle and gun. This is the main equipment that is equipped with each washer. All additional features will facilitate your work, although not significant. If you buy a washing machine for a workshop or company, it is worth paying attention to additional equipment, such as foam nozzles, multi-line, turbochasos, various rotating brushes.
Buying a sink under pressure, we must look at its parameters. The three most important parameters are efficiency, power and water pressure. The pressure in the household car wash ranges from 80 to 160 bar. In professional washers, water pressure usually exceeds 200 bar.
1. Do not have a hermetic working chamber. The impact on the fluid is carried out by the blades of the rotating impeller.
2. Dynamic machines do not have closers. The flow goes continuously from suction to the discharge line.
3. Feed uniform.
A typical example of a bulk machine - a piston pump. Volumetric machines have the following features:
The volume of water in liters per hour. Drive power in pressure washers is from 1, 4 to 3 kW. If you need washer For your own use, and you will not use it too often, its power should not be high. Performance is controlled by flywheel or automatically changes the engine speed. Regardless of the method, high accuracy and repeatability are achieved with a wide range of performance from 10 to 100%. They also work in automatic dosing systems.
They have ball valves made of various materials. In standard conditions, the pump operates with a small flow rate, but it is also suitable for suction Max. 2 meters. They are commonly used on sewage treatment plants and everywhere where important flow measurements are important.
1. The presence of a working chamber in which the displacer affects the liquid (in the blowers) or vice versa, the liquid moves the piston (in engines).
The chamber is periodically in hermetic state, it cuts off from the suction and injection line with the help of closers (valve, plate, gear tooth, etc.).
The electric motor controls the piston through the worm gear and the worm wheel installed in the housing. The worm wheel is installed on the drive shaft, which pushes the piston through the cam. The return of the piston provides a spring located on the piston, which, when moving the piston, driven by the drive, is compressed. The mechanism is immersed in the oil, and the shafts are based on ball bearings. The pump housing is made of cast aluminum and is a monoblock. The monoblock is also a jack and engine connector.
The pump head can be made of several types of stainless steel or plastic. The piston is also made of several types of stainless steel or aluminum oxide. 

Return after the jump is performed using a spring. The diaphragm is appropriately profiled to respond to changes in the stroke and, therefore, change the flow.
The supply of volumetric hydraulic machines is uneven.
Technical indicators of pumps
1. Pump supply - Q
Pump supply is the volume of the fluid supplied to the injection line per unit of time. The feed in the System system is measured in m 3 / s, but more adopted units m 3 / h (for centrifugal pumps) and l / s (for piston pumps).
The electric motor controls the diaphragm through the worm gear and the worm wheel installed in the housing. The worm wheel is installed on the side of the drive shaft, which pushes the shaft connected to the diaphragm through the cam. Return is provided by a spring located on the shaft, which is compressed during the drive movement.
The membrane material is rubber with the liner of the material, and on the side of the liquid is covered with teflon. You want to decide headache without headaches? Twist or pressing the button, and this accessory for 100 grams will work for you tedious work.
2. Pump pressure n
The pump pressure is the increment of the specific energy of the fluid from the entrance to the output of the pump, is measured in meters. The specific energy of the fluid is determined by the expression
where  - specific potential pressure (piezometric pressure);
- specific potential pressure (piezometric pressure);
Satisfaction is guaranteed: the company is engaged only by the highest class products and performs 100% quality control on each finished product. It all begins with two oxygen atoms and one carbon. If we expose these atoms with a pressure of 900 pounds per square inches, the result will be innovative. 25 years ago, this idea appeared, which made a revolution in the traditional swing technique. This simple and rapid solution has become almost instantly known and estimated among cyclists, because the use of carbon dioxide pumps is just as simple and exactly like a siphon.
Z. - specific potential position energy (geometric pressure);
 - specific kinetic energy (high-speed pressure);
- specific kinetic energy (high-speed pressure);
 - liquid density at pumping temperature
- liquid density at pumping temperature
Regardless of whether you want to go to work or go to the mountains, authentic innovation will help you achieve your goals. Perhaps three small atoms do not look great, but when you begin to use them, you will understand how important small things are!
The owner during use becomes especially cold for a short period of time. It is recommended to follow safety procedures. It is small and easy, this is the best choice for circles and competitions. Turning the wheel is easily adjusted using the button, which allows you to quickly solve the problem of soft tires. The intelligent head is universal, it can be used regardless of the type of valve or wheel size.
The expression (2) is the exact formula for the calculation of the pressure. Since the differences of geometric and high-speed heads are small, usually apply an approximate formula
 (3)
(3)
where r n \u003d r nm + p atm is an absolute pressure in the pump discharge nozzle,
R nm - pressure gauge pressure in the discharge nozzle;
Screw the pump head to the pump, install it on the valve, and with the control valve you can apply the pressure with which you rotate the wheel. This solution will help you solve the problem with deflationary rubber in seconds. Using is especially simple: screw the cartridge in the pump handle, install the wheel valve, pull the lever and use the lever to start dosing the pressure on the wheel.
With this method, you can sit in a bicycle saddle in seconds. It can be used both for machine valves and a bathroom. It can also be used in motorcycle tires. You will also find a cartridge out of 16 grams in the package.
R B. = P VM + R atm - respectively for the suction nozzle.
If in the suction pipe of the pump vacuum pressure p centuries,
that P B \u003d RATM - P BB.
Pump pressure N is often called useful, because It is fully spent on pumping, i.e. on the movement of the liquid outside the pump.
3. Pump Pump N.
This power supplied to the pump and measured on its input shaft. For main centrifugal pumps
The plastic housing for the owner allows you to simply and effectively use two functions. The storage case in the pump handle contains two self-adhesive plasters and an adapter with several valve bolts, so it can also be used for vehicle valves or baths. The kit also includes a mounting bracket on the frame with the corresponding screws.
If necessary, it even fits into his pocket. It can also be used for a car valve or bathroom. Due to different capabilities, it creates different pressure depending on the size of the rubber. The patron capacity can be seen in the following table.
 (4)
(4)
where N DV is power supplied to the engine (electrical power);
 - Motor efficiency.
- Motor efficiency.
The main unit of power in the SI - W., derivative of kW.
4. The efficiency of the pump
Efficiency coefficient (efficiency) - the ratio of the useful power of the pump to its power, (summed). KPD - the value is dimensionless.
 (5)
(5)
where 
Centrifugal pumps. Hydrodynamics of the running part.
Device, principle of operation, classification

Figure 3.1 Console type centrifugal pump circuit
The working body of the blade machine is the rotating impeller equipped with blades. Energy from the working KOZ -LES liquid (blade pump) or from a fluid The impeller (blade engine) is transmitted by dynamic interaction of the blades of the wheel with a flowing themliquid.
The paddle pumps include centrifugal and axial.
Figure 3.1 shows the simplest gathering of the centrifugal pump, the flow part of the pump consists of three main elements - supply 1 impeller 2 h Dust 3 The fluid is supplied to the impeller from the supply pipeline.
Assignment of the impeller is the transfer of liquid energy from the engine of the centrifugal pump working wheel consists of a leading aIslave (rim) 6 discs, between which there are blades, curved, as a rule, to the side opposite direction of rotation of the wheel.
The leading drive of the impeller is attached to the shaft. The liquid moves through the wheel from its central part to the periphery. Updated liquid from the impeller to the pressure pipe or, in multistage pumps to the next wheel
Theoretical pump head, Euler formula
In the rotating working wheel on the liquid particles, the centrifugal force is valid:
F.= m. ω 2 R. = ρ∙ V ∙ Ω. 2 R.
Where the FTs centrifugal force
m- mass of particles
ρ - density
V- particle volume
ω-angular speed
R- Radius of the impeller
As a result, pressure drops in the center of the wheel, a vacuum is created, and on the periphery of the wheel, the pressure rises, thereby creating pressure.
The movement of the fluid in the interstopane channels of the rotating wheel can be considered as the result of the addition of two movements: portable (wheel rotation) and relative (movement relative to the wheel).

Therefore, vector absolute speed liquid in the wheel V. may be as the sum of vectors district speed U. and relative speed W. .
Wherein relative speed W. aims on tangent to the blade, and district U. - by tangential to the corresponding circle.
Parallelogram of speeds can be built for any point on the shovel.
If all the values \u200b\u200brelating to the entrance to the shovel, mark the index 1 , and the values \u200b\u200brelating to the exit - by the index 2 , and the angle between velocity vectors and absolutely denoted through , and between tangent to the blade and tangent to the circumference of the wheel spent in the direction, reverse rotation - through , you can get a formula for calculating theoretical pressure (Euler formula)

 (12)
(12)
For the output of the main equation of the theory of the centrifugal pump, the following two assumptions take:
The pump has an infinitely large number of identical blades ( z \u003d. ), and the thickness of these blades is zero ( b \u003d 0.). This assumption means that we assume in the inter-pumping wheels channels such an inkjet flow, in which the shape of all pips in relative motion is completely the same and exactly corresponds to the shape of the blades, and the speeds depend only on the radius and do not change on the circle of this radius. This position can only take place when each elementary stream is sent to its blade.
The efficiency of the pump is equal to one ( =1 ), i.e. There are no all types of energy losses and, therefore, all the power that is spent on the rotation of the wheel is completely transmitted by the liquid, such a pump operation is possible only when pumping the perfect fluid, in the absence of gaps in the pump, as well as in the absence of mechanical friction in the glands and bearings
Such a pump that z \u003d. and = 1 , called An ideal centrifugal pump.
Usually, the liquid is suitable for the impeller's impeller working wheel, and entering the wheel, it comes into inter-pump channels, moving radially it means that the vector V. 1 directed by radius and angle 1 \u003d 90 °. Consequently, the second member in the equation is made equal to zero and the equation takes the form

This form of the Euler equation is more common.
The real wheel of the centrifugal pump has z \u003d 4-8, \u003d 5 - 10 0, \u003d 20 - 40 0.
In this case, the flow in relative movement should not be strictly in the direction of the blades, which carries out to a decrease in the theoretical pressure N. T. Compared to N T∞. .
![]()
where: K - amendment on the conic number of blades,
The coefficient K \u003d 0.6 - 0.8 and depends on the kinematics and the wheel design.
The formula shows that for obtaining high heads using a centrifugal pump, you need to have
first, the larger circumferential speed of the wheel and,
secondly, a sufficient spin of fluid flow with a wheel.
The first is achieved by the corresponding values \u200b\u200bof the number of revolutions and the diameter of the wheel, and the second is a sufficient number of blades, their size and shape.
Unstressed and shock modes of the centrifugal pump
Figure 5.1 shows the unstressed pump operation, when the vector W 1 is directed at the inlet on the spatula, and the outlet of the wheelW 2 is directed along the tangent to the removal spiral.
On the shock modes, the vector W 1 turns relative to
the axis of the blade at the angle of attack 

When streamling the blades and the housing on unstressed mode, there are losses of friction of fluid along the length of H T, even the vortex losses are added on the impact modes, increasing their total value.
The efficiency of the centrifugal pump
Qualitative efficiency takes into account energy losses in the pump that are moving to heat.
 (15)
(15)
where  - Total energy loss in the pump.
- Total energy loss in the pump.
They are divided into three types: hydraulic, mechanical and volumetric.
In fig. 2.5 shows the energy balance in the blade pump to the pump is the power N.Part of this power is lost (turns into heat).
Lost power in the pump is divided into mechanical, volumetric and hydraulic.

General hydraulic losses in the CN, hydraulic efficiency
ABOUT  difference from the types of energy losses in the pump are losses to overcome the hydraulic resistance of the supply of the impeller and the removal, or hydraulic losses.
difference from the types of energy losses in the pump are losses to overcome the hydraulic resistance of the supply of the impeller and the removal, or hydraulic losses.
Fig. 6.1 Triangles of speeds PA input to the impeller with different pump operation modes
When streamlined the blades and the housing on an unstressed mode, there are losses of friction of fluid along the length of H T, even the vortex losses are added on the impact modes (Fig. 6.1), increasing their total value.
General hydraulic losses in centrifugal pumps h is thus equal
h G \u003d H T + H y (9)
The smallest "their value corresponds to the unstressed regime when H y \u003d \u200b\u200b0, H y is the drum losses.
The theoretical pressure of the pump is the pressure, which transmits the blades of the fluid impeller. It is more useful N. There is a connection between them.
N T \u003d H + H g (10)
The ratio of useful pressure to theoretical is called a hydraulic efficiency.
 (11)
(11)
This efficiency takes into account the hydraulic losses in the running part of the centrifugal pumps, which are the largest of all types of losses. The proportion of hydraulic losses in total them is 80-90%.
Full hydraulic losses are estimated as losses in length, and shocks along the entire flow part of the pump, including the supply, impeller, and removal.
Mechanical loss and mechanical efficiency in the TN
Mechanical losses  they are formed outside the flow of the pump and can be determined as the sum:
they are formed outside the flow of the pump and can be determined as the sum:
where  - disc losses;
- disc losses;
 - Loss of mechanical friction in bearings and seals.
- Loss of mechanical friction in bearings and seals.
The latter in the pumps are small and are usually 0.1-0.2% of the power spent.
Disc losses are more significant, which arise as a result of friction of the outer surfaces of the working wheel discs about the liquid between the housing and the wheel.
Disk losses increase greatly with increasing fluid viscosity, while the housing can be heated.
In general, mechanical losses are estimated by mechanical efficiency:
 (19)
(19)
Volumetric losses in the CN. Volume efficiency.
Volumetric losses are associated with power losses when leaks through slotted seals wheels (Fig. 3.3).
The slotted seal scheme is indicated on the RNS.11.1

1 - Case, 2 - impeller, 3 - ring.
Calculation of leaks through a slotted seal is carried out using a hydraulics expiration formula

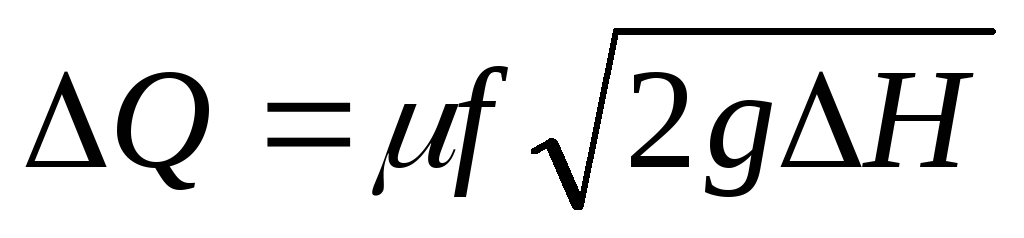 (20)
(20)
In general, leakage in the pump is determined by the volume efficiency:
 (25)
(25)
where Q T is the theoretical supply of the impeller.
Formula full efficiency TN
The total pump of the pump, taking into account the components of the loss, can be represented as follows:
the TE of the pump is equal to the product of hydraulic, volume and mechanical efficiency
Full kpd. The pump is very informative. A deep competent analysis of it in time allows you to judge the level of operation of equipment, in the efficiency of its use.
From tables full kpd. Pumps are equal to:
NPV 150-60 ......... 72%
NPV 5000-120 ...... 85%
Nm 1250- 260 ...... .80%
Nm 10000-210 ...... 89%
Permanent maintaining high value kp.d. Pumps - the main method of saving electricity consumption.
Dependence (26) shows that by the value of kp. A number of factors affect. Analysis of the operation of the main pumps shows that the quantity of kp. Determined by the following main factors:
level of hydrodynamic perfection of the structure;
quality of pump manufacturing and compliance with drawings;
the culture of the pump operation.
The latter requires a good pump assembly with a low level of vibration, maintaining small gaps of target seals, good exploitation of bearings and so on.
Characteristics of the centrifugal pump
The characteristic of the centrifugal pump is the graphic dependence of the pressure of H, the power N and the efficiency from the supply of the pump q with constant revs and the properties of the pumped liquid.
Euler equation looks like

The equation is inconvenient for use in calculations, since it does not contain consumption Q.
You can convert the equation so that the pressure H. T. Express as a flow function Q. and wheel sizes
H. T. = U. 2 / g. { U. 2 - Q. / 2 r. 2 b. 2 tG. 2 }
U. 2 = ω R. 2
If q \u003d 0, then H. T. = U. 2 2 / g. or H. T. = ω 2 R. 2 2 / g.
This equation allows you to build characteristic of the perfect centrifugal pump, Ie, a graph of the pressure of the pressure generated by the pump, from the consumption at the constant number of turns of the wheel.
As can be seen from the equation, the characteristic of such a pump is direct however, the slope of this direct depends on what value the angle of the blade is.
More profitable, and therefore the most frequently used is the blade, bent back, i.e. Such which the angle 2 2 <90°. In most cases, this angle is made approximately 30 °.
For visual constructions of the calculated characteristics of the pump at n \u003d Const. in the coordinate system H. by Q. for n \u003d Const. We appline in the form of two inclined direct theoretical characteristics of the pump with z \u003d. and at the end of the blades z..
Then below the abscissa axis, we construct curves of the change in the two terms discussed above the summary pressure loss in the pump h. 1 and h. 2 . After folding the ordents of these two curves, we obtain the curve of change σ h. us in the flow function. Next, we will deduct σ h. us of H. Tz. And we get a curve H. us \u003d F (Q). The actual characteristic of the pump at the constant number of revolutions.

Curve H. us \u003d F (Q) It is typical for the centrifugal pump.
The characteristic of the pump is usually removed in the bench conditions on cold water. Mode Q 0, which corresponds to the maximum efficiency of the efficiency is called optimal (unstable). There are no shock losses on this mode.
The regime zone in the range of 0.8 q O -1.2 Qau is called the working area. The pump operation is recommended in this zone where the efficiency decreases compared to  no more than 2-3%.
no more than 2-3%.
The fourth curve is applied on the pump characteristic - cavitation characteristic.
Pressure, energy and cavitation characteristics of NM type pumps
according to TU 26-06-1053-76

Figure A.1 - Pump characteristic NM 2500-230, tested on water
Cavitation, cavitation reserve
Cavitation is the phenomenon of a stream of continuity in the place where the pressure becomes equal to or less pressure close to the pressure of saturated vapor of liquid P s.
In this case, the liquid boils, in the cavitation site there are vapor-gas clusters (cavities), which violate the normal structure of the stream. Therefore, arising in the pumps, cavitation primarily worsens the energy indicators H, Q,  .
.
In addition, cavitation causes an increased vibration, and in some cases - erosion of the running part.
In centrifugal pumps, cavitation, first of all, occurs at the entrance to the impact of the impeller from the back side, where the pressure is the smallest.
Quantitative assessment of the cavitation state of the pump is carried out using cavitation stock  ;
;
 (35)
(35)
where  - Energy of liquid
- Energy of liquid
 - Energy of saturated vapor
- Energy of saturated vapor
Cavitational reserve is the excess of the total fluid pressure in the pump inlet nozzle over the pressure of its saturated vapor.
The liquid passing from the entrance to the pump to the low pressure zone loses a portion of the friction pressure and an increase in kinetic energy at the entrance to the blades, so it is necessary to always have a margin of this energy.
Cavitational reserve in which the nuttitious operation of the pump is still possible, is called allowable  .
.
This characteristic is given in the catalogs as the fourth curve of the pump characteristics.
Main parameters of the main pumps of the NM series
|
Mark pump |
Range of change of pump feed, m 3 / h |
Nominal parameters |
||||
|
Feed, m 3 / h |
Extra. Kavit. Stock, M. | |||||
|
0,7 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
1.0 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
1.25 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
0,5 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
0,7 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
1.0 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
1.25 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
0,5 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
0,7 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
1.0 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
1.25 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
0,5 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
0,7 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
1.0 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
1.25 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
0,5 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
0,7 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
1.0 · Q. n. | ||||||
|
1.25 · Q. n. | ||||||
General
Definitions of pressure
Pump pressure (h) - Specific mechanical work transmitted by the pump pumped fluid.Pressure on the pump (h) - Quantitative value characterizing overpressure generated by the pump.
It is usually measured in meters of water column (Usually, when it comes to water column meters, refinement "Water Pillars" Soots). Recently there is a tendency to use as a unit of measurement of MPa (see)
Undercomctions for the operation of the instruments are taken depending on the required flow of fire extinguishing agents, and the rise of terrain and extinguishing devices are determined in each particular case. The loss of pressure in the sleeve lines depend on the type of sleeves, their diameter and quantity, as well as the flow of water passing through their cross-section. Power losses in a hostess line are determined by the formula:
| h p \u003d n r SQ 2, | (2.1) |
where n p - the number of sleeves in the sleeve line (determined by formula 3., or on the basis of real circumstances); S - hydraulic resistance of one pressure sleeve 20 m long (see Pressure Fire Sleeves - NDR resistance); Q - Water consumption passing through a cross-section of a holing line, l / s (determined by the total consumption of water from fire trunks or generators attached to the most loaded sleeve line).
The number of sleeves in the sleeve line is defined as follows:
Calculation for a scheme with one working sleeve line
In the simplest case, when one working sleeve line was laid from one SME, the calculation is carried out in accordance with formula 3..Calculation for a diagram with several sleeve lines
In the case when several (in the overwhelming majority of cases - no more than two) hosted lines were laid from one SMEs, for each of the sleeves, the calculation is calculated according to formula 3.. Then, from the obtained values, the maximum is selected, which is due to the need to ensure the performance of each of the sleeves.| N \u003d MAX (N i n), | (4) |
where, n i n is the desired pressure at the entrance to each of the sleeves.
Calculation for the submission scheme to one device by several sleeve lines
Calculation for schemes with a simple main line
Most sources - for example, or are offered when calculating the required pressure on the SME pump for trunk lines with ramifications, lower the calculation of working lines laid from branching. At the same time, the pressure on the branching is accepted on 10m more than at the device feeding the answer with the highest working pressure. The consumption of water through the cross-section of the main line is made by the amount of expenses in the working lines from the branching of the migrated on this main line.Thus, Formula 3 takes the form:
where, - n p - pressure before the branching, equal:
| N P \u003d N PR + 10, | (5) |
In most cases, this corresponds to reality, however, not always. From the point of view of the hydraulics, to obtain the correct value N R., it is necessary to carry out the calculation of the prescribed pressure of each working line laid from branching and only then make a conclusion about the value N R.. It is dictated by the fact that in some cases (a large number of sleeves in hosted lines, a large consumption from the response devices, the presence of further branch) of the pressure loss in the sleeve lines can noticeably exceed 10m, which will eventually lead to an error of the calculation.
Therefore, the correct formula for calculating the pressure on the SME pump, in which case, it will look like this:
where Z M P is the geometric height of lifting (+) or the descent of the terrain (-) between the level of the pump axis and the location of the branching, m; Max (n R.L.) - the maximum value of the desired pressure at the entrance to each of the sleeve lines connected to the branch.
Calculation for schemes with branching sleeves
In general, the calculation of complex branching trunk lines is reduced to the division of the entire LDCs to the sections for which the calculations in the definition of the maximum required heads at the inlet in the sleeve lines are determined. First, working sleeve lines are calculated, then trunk. Cm. Fig. four.The calculation of such systems is manually, even using Calculators and ECM funds, represents high complexity and is rarely applied in practice.
However, there is a software that allows you to simplify the solution of this task - for example aigs grafis-tactic.
Calculation for several sleeve lines
In schemes with multiple sleeve lines, not always, the required pressure for the operation of the working sleeve lines corresponds to the workload. The fact is that the flow rate from the submission devices is conditionally the same, but the pressure losses also depend on the number and type of sleeves.Consider the following example:
STYLE \u003d "BORDER: SOLID 1PX #CCCCCC; margin-top: 4px; display: inline-block; width: 300px"\u003e
Fig. 5. - An error in choosing a calculated pressure is related to
that the loss of pressure in the sleeve line b.
exceed the pressure loss in the sleeve line a.



