Ventilation systems in country houses. We do natural ventilation in a country house with our own hands
Comfortable living in your own country cottage largely depends on the microclimate created in it. And competent ventilation of the cottage plays an important role in its creation. The ventilation device of the cottage is one of the priority issues that must be considered during its construction. It will not be difficult to create a ventilation system. The main thing is to know and understand the basic principles of action, as well as to be able to make the necessary calculations.
Types of cottage ventilation
Starting the creation and design of ventilation for a cottage, the first thing you have to face is the choice of the type of ventilation. In fact, there are only two of them: natural and forced ventilation. In turn, each of them has its own subspecies, but the main difference lies in the way the air is supplied and removed.
Natural ventilation in the cottage
This type of ventilation implies the creation of a system of vents and ventilation ducts, the principle of which is based on the natural movement of air, which is achieved by the difference in temperature and pressure at the beginning and at the end of the system. The main advantages of natural ventilation are simplicity and low cost of arrangement and maintenance. The disadvantage of such a system is one - as a result of certain weather conditions, for example, in a strong wind, reverse thrust may occur.

Elements of natural ventilation:
- supply and exhaust ventilation ducts;
- air valves and vents.
Forced ventilation in the cottage
Unlike the natural ventilation system, the forced ventilation system of the cottage is based on the use of a special ventilation equipment... The forced system allows high-quality filtering of the incoming air, if necessary, heating or cooling it, regardless of weather conditions. The mechanical system is free from the drawback of reverse thrust. But at the same time, the cost of such a cottage ventilation system is quite high, which, combined with the high prices for its maintenance, makes the forced system an expensive pleasure.

Elements of forced ventilation:
- air intake grille;
- air valve;
- filter;
- air heater or air conditioner;
- fan;
- recuperator;
- silencer;
- air ducts;
- air distributors;
- regulation systems, temperature and air supply sensors;
- fasteners and clamps.

Ventilation according to its purpose can be exhaust, supply or supply and exhaust. This means that the movement of air in rooms is achieved in several ways. Either by air extraction, or by air supply, or both. And if the supply and exhaust system is a purely forced ventilation, then the supply and exhaust ventilation are a hybrid that combines the advantages of natural and forced ventilation systems.
Today during construction country houses and cottages, many seek to make the most of the advantages that technology gives. The result of such actions is the almost complete isolation of the premises from the environment. This, in turn, complicates or almost completely blocks the supply of fresh air. Adding to this the results of human activity, the result is indoor air saturated with carbon dioxide and with excess moisture. That is why it is so important in advance, even at the design stage of the house, to take care of ventilation and create its design scheme, which will organically fit into the overall concept of the cottage.

To create a ventilation system project, you can use specialized programs or execute a diagram on a sheet of paper. In any case, the project should have a detailed ventilation scheme for the cottage with calculations and an indication of the type of ventilation.
The choice of the type of ventilation is, perhaps, the primary task when creating a project. Which of the systems described above to choose depends on where the cottage is located. If it is far from sources of noise and air pollution, for example, a highway or road, then definitely do natural ventilation... It is both cheaper and more expedient from the point of view of a healthy lifestyle. Otherwise, the choice remains with forced ventilation. Also pay attention to the cost of maintenance and the possibility of a constant supply of energy for forced ventilation. As already noted, in comparison with the natural cost of arrangement and maintenance of forced ventilation is many times greater, and not everyone wants to overpay. And the last thing to consider is the volume of ventilated air and the rate of its exchange that this or that system can provide. And for this it is necessary to make calculations, as well as look into SNiP 2.04.05-91.
Ventilation calculations
The ventilation device in the cottage requires certain calculations for the ventilation system. This is a tricky business and requires specialized skills. But if it becomes necessary to do it yourself, then there is a way out. Of course, the accuracy of all calculations will have a certain error, but if necessary, you can consult with a specialist who will point out obvious errors. The calculations themselves for ventilation of the cottage are based on the rates of the air exchange rate, developed on the basis of research for various types of premises. In the table below you can find the main indicators for air exchange:

As follows from the table, for a comfortable stay in a house, it is necessary that the entire volume of air in the premises is completely replaced with clean air a certain number of times during an hour. Based on this table, the total air volume is calculated, which must be replaced within an hour, according to the formula:

An alternative calculation option is the air consumption per person in the room. It is performed according to the formula:

The table below shows the norms for the amount of air per person in 1 m3 per hour:

Based on the data obtained, selection of ventilation equipment, diameter of ventilation ducts and other things. It should be noted that the above data will be sufficient for the selection of equipment and the creation of natural ventilation. Moreover, it has been experimentally proven: for rooms less than 40 m2, ventilation ducts with a diameter of 12 cm allow air exchange in multiples of two volumes. To increase the exchange rate, you can make a channel with a larger section.
For the forced system, it is necessary to calculate the required fan power. This is easy enough. We take the volume of the room and multiply it by the exchange rate. As a result, we get the productive power of the fan. Since forced ventilation is a system of ventilation ducts of a certain length, pressure losses are possible along its entire length, which is fraught with a decrease in the quality of ventilation. Therefore, the fan should be selected with a margin. Using the table below, you can select the equipment with the most optimal performance based on previously obtained data:

Having figured out how to select equipment, let's return to air exchange rate for each room and based on this, we will create the entire ventilation system of the cottage. So, the first thing we do is add up the volume of air exchange per hour for each room. This will be the production capacity of the plant. Channels will depart from it for each room separately. We select the diameter of the supply ducts based on tables.
Having dealt with the air supply, we proceed to its exhaust. The essence is the same as when selecting the supply channels, but one important factor should be taken into account. Power exhaust ventilation should be 10 - 15% more than the supply air. This is necessary so that exhaust air does not accumulate in the room.
Ventilation scheme
Before you make ventilation in the cottage, you will have to draw a drawing of the house by hand or using the program, indicate on it the locations of the supply and exhaust ducts. At this stage, you should stop and clarify some of the rules for the location of ventilation ducts.
For natural ventilation, air vents and valves are located over the windows. Exhaust ducts are located inside the walls of the kitchen, bathroom and toilet. At the bottom of the interior doors, a gap of 10 - 20 mm is made or 2 - 4 air vents are mounted to ensure air movement to the exhaust ducts. All this in a section is displayed on the plan of the house.
Important! For natural ventilation to work properly, exhaust ducts must always be located inside the house. This is due to the very principle of operation of such ventilation. The thing is that if the temperature of the exhaust duct is lower or equal to the temperature outside, there can be no question of any air movement. The exhaust ducts themselves must protrude at least 0.5 m above the roof level. This is due to the pressure difference, which also affects the movement of air.

For forced ventilation, the circuit will look slightly different. On the drawing of the house, it is necessary to indicate the location of the ventilation equipment. The supply channels for each room will be diverted from the air conditioner or heater. We place the air supply points as close as possible to the windows of the premises, and place the exhaust air intake points in the bathroom, kitchen and bathroom. Do not forget about the vents at the bottom of the doors for the movement of air from the supply point to the intake point The ventilation ducts themselves will be placed and hidden in the ceiling or in the walls. But their location should be above the level of the windows.
Cottage ventilation installation
Ventilation in a cottage can be done at the stage of building a house or in an already built one. The difference lies in the complexity and amount of work being done. So the key elements of natural ventilation and forced ventilation ducts are most convenient to create even at the stage of wall construction. They can be immediately hidden in the walls, eliminating the need for various decorative elements. And after finishing, install the remaining ventilation equipment.
The situation is somewhat different if you have to create ventilation in an already built house. It will take more effort. First of all, this will concern the creation of holes in the walls for ventilation ducts, and secondly, the creation of decorative elements that hide the channels themselves. Consider this particular option, since it will fully reveal the features of installing ventilation in a cottage.
Arrangement of natural ventilation
For natural ventilation of the cottage, you will have to do the following:
- at the bottom of the windows, at a level of approximately 15 - 20 cm from the frame, we make holes for the ventilation valves. Their number is taken from the calculation of their throughput and ventilated air volume per hour;

Important! In modern metal-plastic windows, such a valve is installed in the frame itself, in its upper part. But if it is not there, then you have to do everything separately.
- in the doors, at the bottom of the door leaf, we make 3 holes and install ventilation grilles there to allow air to be removed from the room;
- in the premises of the kitchen, bathroom, bathroom we punch a hole in the ceiling and roof. Then we insert the ventilation duct into the resulting hole. At the same time, we make sure that the air intake opening of the channel in the room is at the level of 25 - 30 cm from the ceiling. The channel itself can be fixed to the wall with clamps. The part of the canal located in the attic should be insulated. You can also use a sandwich pipe with insulation;
- on the upper part of the channel protruding above the roof of the house, we install protection against rainfall;

Important! If a natural exhaust system is created, a fan is installed at the beginning of the exhaust duct. The same is done if a supply system is created.
- finally, we install grilles with a mesh at all points of air supply and intake.
Arrangement of forced ventilation
To create forced ventilation, a slightly larger amount of work will have to be done in comparison with natural ventilation. But in general, the stages of work are the same. To create forced ventilation of the cottage, you must do the following:
- in the attic or in a separate room, place and fix ventilation equipment - air conditioner, air heater, and also attach filters to them;

- a hole is made in the wall next to the equipment to install a duct for air intake from the street. The channel itself is connected to the previously installed equipment;
- if the house is one-story, then inside the premises at the air supply points marked on the diagram, we make holes in the ceiling for output ventilation duct;
- then we assemble and install a ventilation duct in the attic and bring it to the hole in the ceiling of the room. Then we put part of the channel inward and install a diffuser with a grill on it;

- in the kitchen, bathroom and toilet we make holes for the outgoing ventilation ducts;
- in the attic we lay channels up to the holes, we put them inside and install a diffuser with a grill;
- all exhaust ducts are led to a chimney with a fan, which we install vertically so that it protrudes 0.5 m above the roof level.
There are times when you have to equip forced ventilation in a house with several floors. Then the ventilation ducts are suspended from the ceiling, and the main duct is arranged in the least noticeable corner of the room. The channels themselves on the ceiling can be hidden using a system of suspended or stretch ceilings. Various materials are used for the ventilation components. Today on the market you can find duct boxes made of plastic and galvanized metal. Metal is of course preferable, but the price for fully metal ventilation of the cottage will be quite high. The most acceptable option would be a combination of metal and plastic parts.
Nowadays, few people build traditional huts with stoves, preferring modern engineering and architectural solutions. As the various and inexhaustible mail shows, ventilation problems in the minds of an ordinary owner of a country house occupy 47th place at best (I hope I will not offend anyone with this statement). And psychologically this is easily explainable: if a city dweller escaped the line of a metropolis and found himself in nature, then he will be provided with something, and fresh air will be provided by definition.

However, the flavors and mown hay will not enter an unventilated house, and that's why:
- Application, doors with a sealed rebate and other structural elements that create an insulating thermal circuit, puts insurmountable barrier to fresh air.
- If there is no air flow no hood through ventilation ducts in bathrooms and in the kitchen.
- As a result, the air in the tightly sealed compartments of the country "submarine" saturated with all kinds of harmthat distinguish modern building materials. The list of dangers includes paints, chipboards, carpets, bedding, etc. Carefully looking around the rooms, you can expand this list yourself.
How much air do we need?
Imagine these numerical air volumes are well known and enshrined in the relevant building codes and regulations. According to SNIP, for living rooms (at the time of the presence of residents there) it is necessary at least one exchange of air volume within 1 hour... That is, if you live in a 16 sq. m and a ceiling height of 3 m, then the owners will need 50 cubic meters of air per hour for a restful sleep. By the way, its weight is 60 kg. During the night in this bedroom it should change up to half a ton. Estimate this figure. Where is the machine that will "drive" 400 cubic meters of air through the room?
The situation is noticeably more serious in public places. SNIP defines that:
- from the kitchen in service mode, at least 60 cubic meters must be removed. m of air per hour,
- from the bath and toilet - 25 cubic meters. m / h;
- the air exchange rate in other rooms, as well as in all ventilated rooms in non-operating mode, should be at least 0.2 room volumes per hour;
- in the gym, billiard room, laundry room, pool and must be served at least 80 cubic meters / h. fresh air;
- comfort in the sauna is achieved when this room is ventilated at the rate of 5 cubic meters / hour for each person;
- in a heat generator (boiler room) - at least 60 cubic meters / hour (in general, ventilation and arrangement of a boiler room is a topic for a completely separate serious article).
Available on some window models special valves for ventilation do not solve the problem radically: the best of them are able to let no more than 20 cubes of air per hour into the house. Those who have studied the previous paragraph, this "twenty" will hardly seem seductive. 
Two versions of climatic comfort
Known 2 ventilation systems: with natural and forced air exchange... The main disadvantage of the first is that the efficiency of its operation depends on variable factors: air temperature, direction and speed of the wind. In order for the draft to work vigorously, the outdoor air temperature must be about 0 ° C or lower, and the minimum difference between the level of air intake in the premises (i.e., the height of the installation of the supply grilles or at least the air vents) and its release (the height of the head or ventilation duct) - not less than 3 meters.
For a one-story dacha, this is not at all typical. As soon as it gets warmer outside, such a system stops working altogether.
I recall the sizzling summer of 2010, which I spent in a one-story frame house with a fairly high ventilation pipe. The result of natural ventilation in heat is zero. You bring a sheet of paper to the edge of the channel, but it does not move. Those. hopes for natural ventilation just when it is desperately needed were completely dispelled.
Therefore, in order to provide climatic comfort in the country, it is equipped forced mechanical ventilation systemsindependent of temperature fluctuations in the outside air and the height of the ventilation pipe.

Mechanical ventilation is especially needed in rooms that are problematic in terms of temperature, humidity and odors: boiler rooms, built-in garages, laundry rooms, workshops.
Removing stagnant air: forced ventilation
The simplest version of forced ventilation includes active exhaust and natural inflow... In it, polluted air is mechanically evacuated outside the house. For this, various kinds are used. paddle fans... They create a slight vacuum at the edge of the ventilation duct, which draws out the polluted air from the premises.
To replace it, according to the laws of physics about the equality of pressures in communicating vessels, fresh air enters through the slightly open windows (or slots in them), a gap under the door, etc. For stable operation of such ventilation, it is necessary atmospheric connectivity... Doors with a sealed rebate should be at least ajar. With the windows and doors closed, the polluted air from the country house will not go anywhere: the fans, even if they are turned on at full capacity, will "choke" and fail ahead of time.

Here it is appropriate to talk about providing individual hood in the toilet and bathroom, in the kitchen, as well as in technical rooms. Installed in them local fans by design are divided into axial and centrifugal... Their work schedule depends on the purpose of the ventilated premises.
Agree, why waste the fan in the bathroom while there is no one there? No need at all! Therefore, such fans are equipped with different (according to the principle of operation) sensors - motion, humidity, etc. In the toilet, for example, it is reasonable to connect the fan to a switch.

However, even such a seemingly simple thing has its own nuances. So, for obvious reasons, it is advisable to extend the operation of the toilet fan by 5-10 minutes after turning off the light. A simple time switch included in the fan's electrical circuit will solve this delicate problem.
Wall fans remove air through ducts provided in the walls during the construction of the house. If you are building a house from scratch, then the project should include the possibility of optimal ventilation of the premises. To do this, it is better not to "scatter" on the local, but to install in the back room or in the attic central exhaustfan, one for the whole dacha. It is connected to the objects of the hood by air ducts. For the central exhaust fan, it is structurally used centrifugal circuitcapable of "shoveling" air from several suction ducts. Such devices have a reduced noise level, but still it is better to place them away from the bedroom and nursery.
Blowing in both directions: supply and exhaust ventilation systems
It is difficult to find flaws in the considered systems in warm weather, but they are revealed with the arrival of cold weather. The fact is that the air goes inside in winter without preheating. Of course, this leads to drafts and local hypothermia of rooms. Both in winter and in summer such systems not designed to remove dust and odors from the air... This set of shortcomings led to the creation of a more perfect supply and exhaust ventilation systems... It supplies a sufficient amount of cleaned and, if the weather requires it, heated fresh air. And the waste is removed with the help of fans.
It is reasonable to install such ventilation systems in houses in the vicinity of motorways. They will not allow the stench of the car to poison the dacha life. Such installation is required in rooms with a swimming pool. But the creation of a comfortable microclimate in them is a large separate topic that we will not consider today.
For forced supply of fresh air, it is reasonable to use factory monoblock air handling units, and not engage in amateur performances. Although creative and skilled summer residents may disagree with me. For this we respect them.
Installations are installed in the attic or outside the house. After cleaning and heat treatment, the air enters the rooms through the duct network. The location of the air ducts should also be provided at the design stage. Most often they are placed behind a false ceiling. And this "eats up" 10-15 cm of the height of the room.
Often, in tandem with a supply unit, they are used roof exhaust fan... Of course, the supply unit and the exhaust fan must "pull" synchronously, otherwise there will be either increased or decreased pressure at the dacha.

Moving on to serious technologies. That is, not "clumsy" distillation of air from empty to empty, but to the careful use of thermal energy accumulated in the house. This is a ventilation system based on an energy-saving air handling unit with a plate recuperator or a rotary heat exchanger.
Traditionally, the unit is mounted in the attic. For air exchange, 2 air duct networks are built:
- Air intake from the garden, as well as its delivery from the installation to the premises, goes through the network supply air ducts.
- The air from the premises is returned to the supply unit.
- And then goes outside the building through the network return ducts.

Air handling units with a recuperator reduce the cost of heating the supply air by 10-70%. They are based on a plate cross-flow recuperator - a package of thin metal plates, between which gaps are left. The air removed from the room flows into every second gap between the plates, and fresh air flows through the remaining channels. Since the plates are very thin, they easily transfer heat from a heated air stream to a colder one.
Air handling units with rotary heat exchangers imported production - the pinnacle of ventilation with maximum energy savings. But they are quite expensive and have not yet received distribution in ordinary dachas. 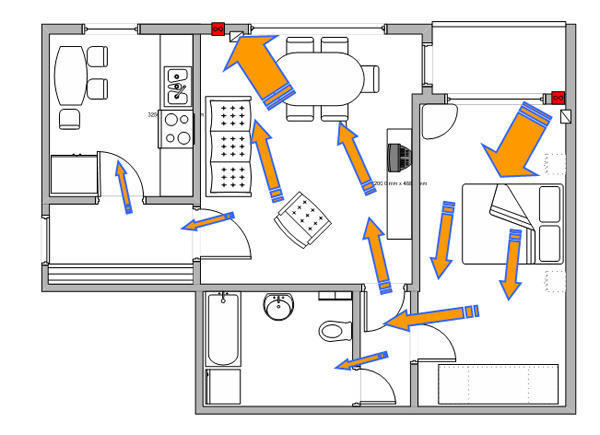
However, I would like to close the article with an encouraging story about a wonderful domestic development, worthy of being embodied in metal. It was created in industrial Omsk, at the Ecoterm enterprise. The unit is called UVRK-50. To understand the essence of her work, one can draw an analogy with how we breathe in severe frost - through a warm woolen muffler. When you exhale, part of the heat and moisture is given to it, and when you inhale, fresh air, passing through the matter, absorbs heat and moisture and returns them to the body. This ensures ventilation of the lungs with optimal energy savings.
When using this system, joint operation of two units in adjacent rooms... They alternately automatically switch on the different direction of flow and provide fresh, clean air for an apartment of 60 sq. m with minimal energy loss... Power consumption does not exceed 30 W, and the noise level is 42 dB.

The unit's inlets are lined with gratings located both in the interior and on the facade of the summer cottage.
The development of this design by Siberian craftsmen was prompted by the unsatisfactory, I would say, the ugly state of the air in rooms with closed double-glazed windows. And although UVRK-50 was created for urban conditions, there are no restrictions for its use in summer cottages. 
Here is a suburban light version of the supply and exhaust ventilation. Honor and praise to these engineers!
And what about the ventilation in your country house?
The article is posted in sections:
Proper ventilation of your home is important part maintaining a healthy atmosphere means controlling air purity, temperature and humidity. We spend half of our life at home, and we just need clean indoor air, and not only us - ventilation is able to preserve the building for many years, protecting building materials from mold, and the interior of the house from dirt and dust. We will tell you what ventilation systems are, about their use in every room of the house.
What is Sick Building Syndrome?
The fact is that a poorly ventilated building can be hazardous to the health of residents. it headache or dizziness, chronic fatigue, irritability, insomnia, dry cough, and other diseases. However, laboratory tests do not show significant changes, and cough treatment does not lead to improvements. All these signs are associated with sensitivity to environmentincluding microorganisms and chemicals in the air at home without proper ventilation.
Without ventilation, your house is "sick" too, it is mold, fungi, destruction building materials - stone and wood. The appearance of insects and other pests. Do-it-yourself ventilation of a country house creates all the conditions for a comfortable stay. For a country house, you can use two main types of ventilation systems. More about them.
video
Passive ventilation (natural)
Natural ventilation in a country house is created through open windows, doors, vents and other openings. The size and location of the ventilation openings directly affect the ventilation efficiency. Where cooling is required, windows and other openings in the upper level of the house can be opened so that warm air will escape. In winter, well thought out passive ventilation freshens the air without creating drafts or releasing too much heat.
In a house in which only passive ventilation is present, all windows and doors are often open in summer, the more openings in the room, the more the air is purified. Natural ventilation at home does not differ in a special installation, open openings - and there is its "installation". However, you should pay attention to the tips to ensure a clear air flow.
louvers integrated into the ventilation openings ensure low level ventilation for a long time without creating drafts.
a different way of opening the windows will help control the air flow. For example, full side opening of the window will increase the air breeze, while the "window" will decrease.
if your house has more than one floor, make sure the windows are open on all floors, as hot air rises up and it may turn out that the air is clean and fresh only below.
the mosquito net will not only keep your children safe, but will also keep the windows open throughout the summer at any time of the day.
remember to ventilate the floor through the floor to get rid of dampness.
Active ventilation system (artificial)
Unfortunately, the natural ventilation of a country house is limited, a comfortable temperature is often not created quickly enough, air is supplied with dust particles. Artificial ventilation does not have such disadvantages. Active ventilation is mechanical ventilation of the building. Exhaust and supply fans are powered by electricity than more system and its components, the more energy it will use.
Exhaust fans are designed to remove and purify air from kitchens, bathrooms and laundries. It is important to choose a suitable exhaust fan, because some cannot completely remove humid air. The hood does not bring clean air, but only takes it in; you will have to use additional methods of obtaining air, for example, opening the windows.
Supply and exhaust ventilation
This is the most suitable method of artificial ventilation, supply and exhaust ventilation makes it possible to fully meet all ventilation requirements at home. This system not only draws in air, but also gives it an influx. Often used for office and residential applications.
Mechanical supply and exhaust ventilation provides constant controlled air exchange, can have the functions of cooling, heating and humidifying the air. Several rooms can enter the comfort zone from the main unit of the supply and exhaust system. Do-it-yourself ventilation of a country house may seem simple, however, mistakes often arise that should not be made.
installation of a recuperator in an unheated room. If you choose to use this ventilation system, make sure the room temperature is at least 8 ° C above freezing to ensure maximum ventilation.
the windows are not tightly closed. This will result in a loss of energy and warm air.
no insulation, incorrect installation of ventilation ducts.
the main conditions for the proper operation of the ventilation system are thorough isolation, connection and installation of channels, otherwise the lack of stable operation is demonstrated.
installation without a circuit. The ventilation scheme of a country house should be drawn up in advance, installation work for each house is calculated here individually, what power is needed for the air flow for each of the rooms where the ventilation points will be located.
lack of system adjustment. For each season, its own air supply is determined, so in summer the recuperator is set to cooling mode. The main indicator of misadjustment is your windows. Damp windows in winter or summer are a sign of high humidity, which ventilation does not remove well enough.
So, let's summarize. You have become aware of the basic, available ways to improve ventilation in the house. Perhaps this will not be enough, for this there is a video in this article, which shows how to install a supply and exhaust ventilation system.

For ventilation in a country house, a supply and exhaust unit with heat and moisture recovery ZENIT 1000 SW was used.
The installation serves a house of 250 m2. Installation, mounted in a heated garage, on the first floor of the house.
Vacation home it is heated by a heat pump, which allows it to heat up the house in winter and cool it down in summer. Therefore, instead of a conventional water heater, a water cooler was installed in the unit, which operates as a heater in winter and as a cooler in summer.
For maintaining constant humidity in the house, an ultrasonic humidifier was connected to the unit.
Ventilation system calculation
The ventilation in the house was calculated according to the following algorithm:
- first, we calculated the air exchange and selected the cross-section of the air ducts;
- then the type of ventilation system (with recuperation) was selected;
- then they made a ventilation project in a private house - they determined the place of installation of ventilation equipment (installations and units), the places for the intake of fresh air and the release of exhaust air, as well as the places where the air ducts will pass.
Exhaust air is best discharged above the roof, and the inflow can be carried out anywhere, but at least two meters from ground level or surface.
When calculation of ventilation and air conditioning in the house the main criterion is always a person's comfortable stay in the house. To ensure a comfortable climate in the house, it is important not only the availability of fresh air and its temperature, but also the speed of air flows from the grilles and inside the channels. The lower the flow rate, the quieter the acoustic noise from indoor ventilation and there are no drafts. Air exchange in a house with an air handling unit is greater than in a room with natural ventilation. This is due to different regulations in ventilation systems. For mechanical ventilation, they are 5 m3 / hour, for natural ventilation 1 m3 / hour, that is, less. therefore natural ventilation at home creates more comfortable conditions for a person. But natural ventilation is not able to ensure normal air exchange in a large house, since the duct area will be very large. Therefore, with large areas of the house and, accordingly, a large hood, it is necessary to resort to mechanical hood. In this case, the flow of air is no longer possible to organize in a natural way.
For good air exchange in the house, transfer grilles are installed in the doors so that the air moves freely through the house from the supply grilles to the exhaust grilles. The air flow is considered to be organized correctly if the last room in the air movement is a toilet, laundry, bath or other room. That is why the hood is usually installed in the kitchen, bathroom or toilet. If there is no lattice or gap under the door, then the ventilation in the house can be considered not working. There may also be problems opening or closing the door due to the differential pressure that the ventilation system creates.
Supply ventilation system installed in the house consists of ventilation unit, an additional filter unit for deep filtration of the supply air, a humidifier and a ventilation network.
The ventilation equipment includes:
- air damper with a drive;
- filter;
- water heater;
- fan;
- enthalpy recuperator;
- muffler.
And the network includes an air intake grille, air ducts and air distribution devices (grilles, diffusers, anemostats). A set of supply ventilation equipment is shown in the figure below. Filter in the supply ventilation system It is necessary to remove large dust particles that are present in the outdoor air. Air heater - for heating air in the cold season, they are not available in all systems, they are installed at the request of the customer and can be water and electric.
When using water heaters, the ventilation system must be additionally equipped with mixing units (hydraulic piping of the heater), which in turn increases the cost of the system.
Additionally on the topic:
Country house pool ventilation
Even at the design stage of a country house, you should consider which system will be able to serve this room with high quality. It should not be forgotten that the pool is the most aggressive environment for the structure itself. Therefore, a ventilation system must be present. Today the market offers a large selection of modern climate systems capable of providing a high level of comfort.
The article will cover types of ventilation systems, their pros and cons, what structural elements the ventilation system consists of, and you will also learn how to mount supply and exhaust ventilation system.
As you know, fresh, clean air, saturated with oxygen, has a beneficial effect on human health, and a well-designed and installed ventilation system will provide comfortable living inside an enclosed space.
According to SNiP 2.08.01-89 * Appendix 4, the amount of air removed is:
For living rooms - 3 m 3 / h per 1 m 2;
For kitchen:
With a 2-burner stove - 60 m 3 / h;
With a 3-burner stove - 75 m 3 / h;
With 4-burner hob - 90 m 3 / h.
For a bath - 25 m 3 / h;
For a restroom - 25 m 3 / h;
For a combined room of a toilet and a bathroom - 50 m 3 / h;
Accordingly, the volume of incoming outdoor air must be equal to the volume of air removed from the room. For living rooms (living rooms, bedrooms), the flow of fresh air must be at least 30 m 3 / h per person.
Types of ventilation systems
There are two types of room ventilation systems: natural ventilation and forced ventilation.
Natural ventilation premises is carried out due to the temperature difference between the outside and inside air. As you know, the density of cold air is greater than the density of heated air. This causes the cold air to sink downward, displacing the warm air. This creates a pressure difference between the outside and inside air. Due to this pressure difference, the cold outside air tends to the low pressure zone, i.e. into a room with warm air, and warm air is forced out of the room and rises through the ventilation duct to the outside. This creates a draft in the ventilation duct. This is how the natural ventilation system works.
Pros of natural ventilation :
Cheap to install and operate;
Easy installation;
Doesn't break;
Does not depend on electricity.
Cons of natural ventilation :
Has a limited capacity regulation, it is regulated only in the direction of capacity reduction;
Large heat loss during the operation of natural ventilation in winter;
Natural ventilation cannot work in summer, because the air temperature inside and outside is almost the same;
There is no air filtration.

Forced ventilation of premises works thanks to the creation of artificial fresh air flow by fans and artificial draft in the exhaust duct. This system allows you to completely control the air exchange in the room. But the efficiency of forced ventilation depends entirely on the availability of electricity in the house. If for some reason there is no electricity in the house, the forced ventilation will immediately stop working. Therefore, such ventilation requires a backup power supply in the house.
Advantages of supply ventilation :
Performance adjustment, both upward and downward;
The supply ventilation efficiency does not depend on the outside air temperature;
Filtration, heating, cooling, humidification and dehumidification of air;
Minimal heat loss due to heating of cold outside air.
Cons of supply ventilation :
Forced ventilation does not work if there is no electricity in the house;
Additional energy costs, periodic filter replacement;
Supply ventilation elements may fail;
Requires soundproofing, because makes some noise.
Considering all the above pros and cons of natural and forced ventilation, as well as the costs of materials and installation of ventilation, choose the most suitable view ventilation.
Elements of the ventilation system

Natural ventilation system consists of the minimum required structural elements: supply valvethrough which fresh air enters the room (as an alternative to the supply valve, an open window can act) and chimneythrough which the exhaust air is discharged to the outside. A deflector is installed above the chimney.


Is a device that increases traction in ventilation pipe, creating a zone of reduced pressure around itself due to the design features, thereby sucking air from the chimney. These are all the elements that make up natural ventilation.
Forced ventilation consists of a much larger number of components. The entire forced ventilation system is centered around one important element - supply and exhaust unit... This block carries out both the supply of fresh air and the removal of exhaust air.

Consists of the following elements: supply fan, extract fan, recuperator, air heater, bypass and filters... Let's take a closer look at how these seemingly complex elements work.
FROM supply and exhaust fan everything is clear, one pumps air into the room, and the other takes out the "dirty" air outside. Supply air filter prevents dust, insects, pollen, etc. from entering the house and the ventilation system itself. Extract air filter protects the supply and exhaust unit from house dust getting into it, thereby increasing its service life. After the fans and filters, the air enters the recuperator.

Recuperator or the heat exchanger heats the incoming cold air with the warm exhaust air without mixing the incoming and outgoing air flows. This is achieved due to the close arrangement of the supply and exhaust ducts. Thanks to the recuperator, heat loss at home is significantly reduced.
As you know, in close interaction of air flows with positive and negative temperatures, condensation forms. And this condensate is formed, of course, in the recuperator. At rather low outdoor temperatures, this condensate freezes, forming ice in the recuperator ducts. This ice can clog and damage the channels. To prevent this from happening, we added bypass, which allows you to direct cold air bypassing the recuperator. Thanks to the bypass, the heat exchanger is heated by the warm extract air and the ice formed in it melts.
Even when passing through the recuperator, the cold air does not heat up enough to ensure comfortable living in the house. Therefore, after the recuperator, there is a heating element called air heaterwhich heats fresh air to a comfortable temperature.
Some expensive block models have built-in humidifiers, for humidification of dry winter air.
The supply and exhaust unit has a control and automatic regulation system that allows you to set certain values \u200b\u200bof air temperature, air flow rate, degree of air humidification.
It is advisable to place the supply and exhaust unit in the attic of the house so that the length of the air ducts is minimal.
Air ducts in cross-section they differ into round and rectangular. Round air ducts have less resistance when air flows through them, which in turn reduces pressure losses in the system and reduces noise.

Rectangular air ducts have more resistance than round ones, but they take up less space and their use is justified when the space for ventilation is limited.


Also, air ducts differ in material and are metal, plastic, metal-plastic, foil and textile. When choosing air ducts, consider the environment in which they will be used: temperature and humidity.
To determine the size of the ducts, consult with specialists.

When installing air ducts, various shaped products: tees, crosses, bends for changing the direction of the duct, adapters from one duct diameter to another, adapters with round section rectangular, plugs, nipples for connecting air ducts, etc.


And finally, at the outlet from the supply ventilation duct, a anemostat - a device that evenly distributes the air flow coming from the duct throughout the room.
Installation of the supply and exhaust ventilation system
The design of the ventilation system should begin at the design stage of the house, because air ducts suspended from the ceiling and covered with stretch or suspended ceilings will subtract 15-20 cm from the total height of the room. When placing the air ducts inside the wall frame, the thickness of the walls should be taken into account at the design stage of the house.
Air inlet and the deflector must be placed at a distance of at least 10 meters, ideally the air intake is on one side of the house, and the deflector on the other.
The air intake opening is placed at a height of at least 1.5 m so as not to entrap radioactive soil gas radon into the ventilation system, which negatively affects human health. The ventilation inlet itself is covered with a net to prevent leaves, insects, birds, etc. from entering the ventilation system.
Air outlets placed in places of high air pollution: kitchen, bathroom, toilet. In the kitchen, an inflow of fresh air is not needed, only an exhaust hood. Each living room must have a separate supply air duct.
For each of the rooms, a separate air duct should be installed to remove the exhaust air, i.e. air outlets from different rooms should be connected by air ducts in parallel, and not in series, then the smell from the toilet will not appear in the kitchen, and the smell from the kitchen and toilet will not appear in the bedroom. Thus, all air exhaust ducts should be connected directly before the exhaust opening of the supply and exhaust unit.

Rigid ducts should not be connected directly to the ventilation unit, otherwise vibration and noise from the unit will be transmitted through the ducts to the room. Therefore, it is necessary to connect rigid air ducts and the unit only through flexible corrugated air ducts and the length of the flexible section must be at least 1 m.

All air ducts are glued with a layer thermal insulation 10-15 mm thick. This will avoid moisture condensation in the duct and prevent noise and vibration from being transmitted through the duct.
Try to place the ducts with the smallest angle of rotation, because air ducts located at right angles sharply reduce the pressure in the system and thereby reduce the efficiency of the ventilation system. In addition, the pressure in the system decreases as the length of the ducts increases, so the duct length should be kept to a minimum.

Fastening circular ducts carried out using a clamp with a hairpin (c), or using punched tape (d). Fastening of rectangular air ducts produced byZ -shaped (b) orL -shaped profile (a) and pins, or using a traverse and pins (e).
Supply and exhaust ventilation unit it is advisable to place it in the center of the house in the attic so that the air ducts have a minimum length. It is also necessary to provide free access to the ventilation unit, because filters are periodically changed and maintenance block.
That's all you need to know at the initial design stage. ventilation systems in a private house... Subscribe to new articles in which you will find out even more useful and detailed information about ventilation systems for country houses.
Do you want to receive new articles by mail?